 |
rssoft
0.0.0
Reed-Solomon codes library with soft decision decoding
|
 |
rssoft
0.0.0
Reed-Solomon codes library with soft decision decoding
|
#include <GSKV_Interpolation.h>
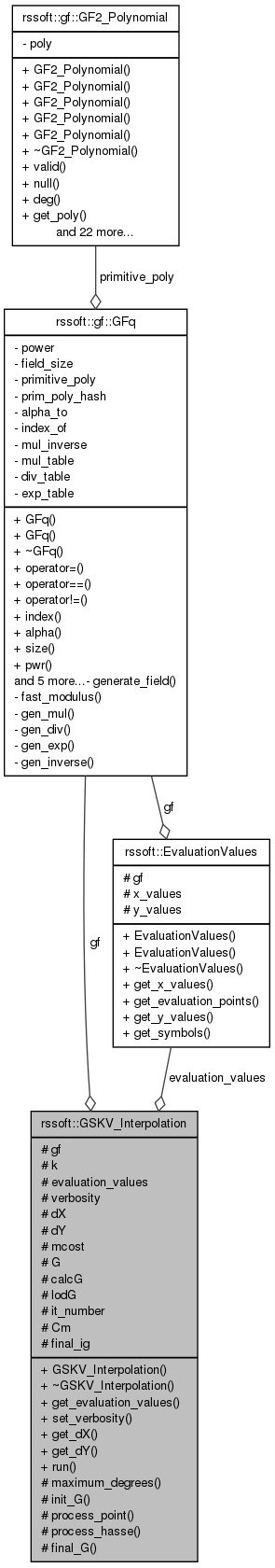
Public Member Functions | |
| GSKV_Interpolation (const gf::GFq &_gf, unsigned int _k, const EvaluationValues &_evaluation_values) | |
| ~GSKV_Interpolation () | |
| const EvaluationValues & | get_evaluation_values () const |
| void | set_verbosity (unsigned int _verbosity) |
| unsigned int | get_dX () const |
| unsigned int | get_dY () const |
| const gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial & | run (const MultiplicityMatrix &mmat) |
Protected Member Functions | |
| std::pair< unsigned int, unsigned int > | maximum_degrees (const MultiplicityMatrix &mmat) |
| void | init_G (unsigned int dY) |
| void | process_point (unsigned int iX, unsigned int iY, unsigned int multiplicity) |
| void | process_hasse (const gf::GFq_Element &x, const gf::GFq_Element &y, unsigned int mu, unsigned int nu) |
| const gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial & | final_G () |
Protected Attributes | |
| const gf::GFq & | gf |
| Reference to the Galois Field being used. | |
| unsigned int | k |
| k factor as in RS(n,k) | |
| const EvaluationValues & | evaluation_values |
| Interpolation X,Y values. | |
| unsigned int | verbosity |
| Verbose level, 0 to shut down any debug message. | |
| unsigned int | dX |
| unsigned int | dY |
| unsigned int | mcost |
| Multiplicity matrix cost. | |
| std::vector < gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial > | G |
| The G list of polynomials. | |
| std::vector< bool > | calcG |
| Li Chen's optimization. If true the corresponding polynomial in G is processed. | |
| std::vector< unsigned int > | lodG |
| Leading orders of polynomials in G. | |
| unsigned int | it_number |
| Hasse derivative iteration number (inner loop) | |
| unsigned int | Cm |
| Cost of current multiplicity matrix. | |
| unsigned int | final_ig |
| Index of the result polynomial in G list. | |
| rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::GSKV_Interpolation | ( | const gf::GFq & | _gf, |
| unsigned int | _k, | ||
| const EvaluationValues & | _evaluation_values | ||
| ) |
Constructor
| _gf | Reference to the Galois Field being used |
| _k | as in RS(n,k) |
| _evaluation_values | Evaluation X,Y values used for coding |
Destructor
{}
| const gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial & rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::final_G | ( | ) | [protected] |
Finalize process with G list of polynomials and find result polynomial
< index of polynomial in G with minimal leading order
< minimal leading order of polynomials in G
{
bool first_g = true;
unsigned int ig_lodmin = 0;
unsigned int lodmin = lodG[0];
unsigned int ig = 0;
std::vector<gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial>::const_iterator it_g = G.begin();
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, "it=" << it_number << " final result" << std::endl);
for (; it_g != G.end(); ++it_g, ig++)
{
/*
if (it_g->is_in_X()) // Circumvent design flaw where an X solution only can be returned which cannot be factorized. (Is this a design flaw?)
{
//DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, "g_" << ig << " is a polynomial in X only" << std::endl);
std::cout << "g_" << ig << " is a polynomial in X only with LOD = " << lodG[ig] << std::endl;
continue;
}
*/
if (first_g)
{
ig_lodmin = ig;
lodmin = lodG[ig];
first_g = false;
}
if (lodG[ig] < lodmin)
{
lodmin = lodG[ig];
ig_lodmin = ig;
}
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, "o G_" << it_number << "[" << ig << "] = " << *it_g << std::endl);
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, " lod = " << lodG[ig] << std::endl);
}
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, "Minimal LOD polynomial G_" << it_number << "[" << ig_lodmin << "]" << std::endl);
//std::cout << "Min LOD = " << lodmin << std::endl;
return G[ig_lodmin];
}
| unsigned int rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::get_dX | ( | ) | const [inline] |
{
return dX;
}
| unsigned int rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::get_dY | ( | ) | const [inline] |
{
return dY;
}
| const EvaluationValues& rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::get_evaluation_values | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Get the X evaluation points used to calculate candidate codewords (horizontal or column matrix wise)
{
return evaluation_values;
}
| void rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::init_G | ( | unsigned int | dY | ) | [protected] |
Initialize G list of polynomials and related lists
| std::pair< unsigned int, unsigned int > rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::maximum_degrees | ( | const MultiplicityMatrix & | mmat | ) | [protected] |
Interpolation polynomial maximum degrees
{
float fdX, fdY;
fdY = floor((1+sqrt(1+((8*mmat.cost())/(k-1))))/2.0f) - 1.0;
fdX = floor((mmat.cost()/(fdY+1)) + ((fdY*(k-1))/2));
return std::make_pair((unsigned int) fdX, (unsigned int) fdY);
}

| void rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::process_hasse | ( | const gf::GFq_Element & | x, |
| const gf::GFq_Element & | y, | ||
| unsigned int | mu, | ||
| unsigned int | nu | ||
| ) | [protected] |
Process a Hasse derivative. This is the inner iteration of the algorithm
| x | Evaluation point in GFq |
| y | Value in GFq at evaluation point |
| mu | Mu parameter of Hasse derivative (related to X) |
| nu | Nu parameter of Hasse derivative (related to Y) |
< index of polynomial in G with minimal leading order
< minimal leading order of polynomials in G
< evaluations of Hasse derivative at (x,y) for all polynomials in G
< G list for next iteration
< Leading orders of polynomials in G_next
< indicator character for debug display
{
unsigned int ig_lodmin = 0;
unsigned int lodmin = 0;
bool first_hnn = true;
std::vector<gf::GFq_Element> hasse_xy_G;
std::vector<gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial> G_next;
std::vector<unsigned int> lodG_next;
bool zero_Hasse = true;
std::string ind("");
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, "it=" << it_number << " x=" << x << " y=" << y << " mu=" << mu << " nu=" << nu << " G.size()=" << G.size() << std::endl);
// Hasse derivatives calculation
unsigned int ig = 0;
std::vector<gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial>::const_iterator it_g = G.begin();
for (; it_g != G.end(); ++it_g, ig++)
{
if (calcG[ig]) // Polynomial is part of calculation as per Li Chen's optimization
{
gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial h = dHasse(mu, nu, *it_g);
hasse_xy_G.push_back(h(x,y));
unsigned int wd = it_g->wdeg();
if (hasse_xy_G.back().is_zero())
{
ind = "=";
}
else
{
zero_Hasse = false;
ind = "!";
// initialize polynomial localization variables
if (first_hnn)
{
lodmin = lodG[ig];
ig_lodmin = ig;
first_hnn = false;
}
// locate polynomial in G with minimal leading order
if (lodG[ig] < lodmin)
{
lodmin = lodG[ig];
ig_lodmin = ig;
}
}
}
else // Polynomial is skipped for calculation due to Li Chen's optimization
{
ind = "x";
hasse_xy_G.push_back(gf::GFq_Element(gf,0));
}
// debug print stuff
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, ind << " G_" << it_number << "[" << ig << "] = " << *it_g << std::endl);
if (calcG[ig])
{
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, " D_" << it_number << "," << ig << " = " << hasse_xy_G.back() << std::endl);
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, " lod = " << lodG[ig] << std::endl);
}
else
{
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, " lod = " << lodG[ig] << std::endl);
}
}
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, "Minimal LOD polynomial G_" << it_number << "[" << ig_lodmin << "]" << std::endl);
if (zero_Hasse)
{
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, "All Hasse derivatives are 0 so G_" << it_number+1 << " = G_" << it_number << std::endl);
}
else
{
// compute next values in G
it_g = G.begin();
ig = 0;
for (; it_g != G.end(); ++it_g, ig++)
{
if (calcG[ig]) // Polynomial is part of calculation as per Li Chen's optimization
{
if (hasse_xy_G[ig].is_zero())
{
G_next.push_back(*it_g); // carry over the same polynomial
lodG_next.push_back(lodG[ig]);
}
else
{
if (ig == ig_lodmin) // Polynomial with minimal leading order
{
gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial X1(1,k-1);
X1.init_x_pow(gf,1); // X1(X,Y) = X
G_next.push_back(hasse_xy_G[ig]*(*it_g)*(X1-x));
unsigned int mX = it_g->lmX(); // leading monomial's X power
unsigned int mY = it_g->lmY(); // leading monomial's Y power
lodG_next.push_back(lodG[ig_lodmin]+(mX/(k-1))+1+mY); // new leading order by sliding one position of X powers to the right
}
else // other polynomials
{
G_next.push_back(hasse_xy_G[ig]*G[ig_lodmin]-hasse_xy_G[ig_lodmin]*(*it_g));
lodG_next.push_back(std::max(lodG[ig],lodG[ig_lodmin])); // new leading order is the max of the two
}
}
if (lodG_next.back() > Cm)
{
calcG[ig] = false; // Li Chen's complexity reduction, skip polynomial processing if its lod is too big (bigger than multiplicity cost)
}
}
else // Polynomial is skipped for calculation due to Li Chen's optimization
{
G_next.push_back(*it_g); // carry over the same polynomial
lodG_next.push_back(lodG[ig]);
}
}
// store next values if matrix cost is not reached
if (it_number < mcost)
G.assign(G_next.begin(), G_next.end());
lodG.assign(lodG_next.begin(), lodG_next.end());
it_number++;
}
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 1, std::endl);
}

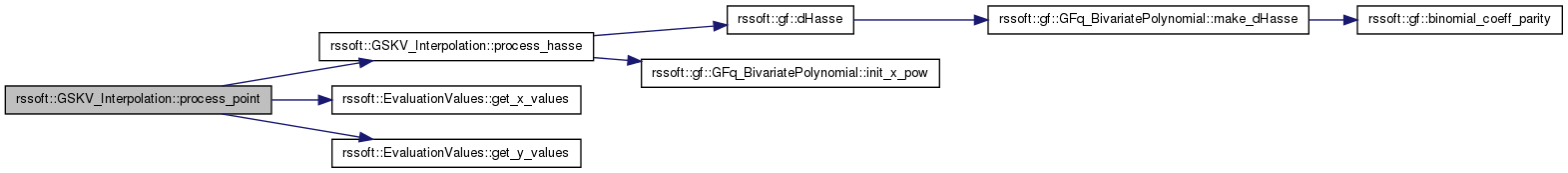
| void rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::process_point | ( | unsigned int | iX, |
| unsigned int | iY, | ||
| unsigned int | multiplicity | ||
| ) | [protected] |
Process an interpolation point with multiplicity. This is the outer iteration of the algorithm
| iX | X coordinate that is evaluation point in GFq |
| iY | Y coordinate that is value in GFq at evaluation point |
| multiplicity | Multiplicity |
{
for (unsigned int mu = 0; mu < multiplicity; mu++)
{
for (unsigned int nu = 0; nu < multiplicity-mu; nu++)
{
process_hasse(evaluation_values.get_x_values()[iX], evaluation_values.get_y_values()[iY], mu, nu);
}
}
}
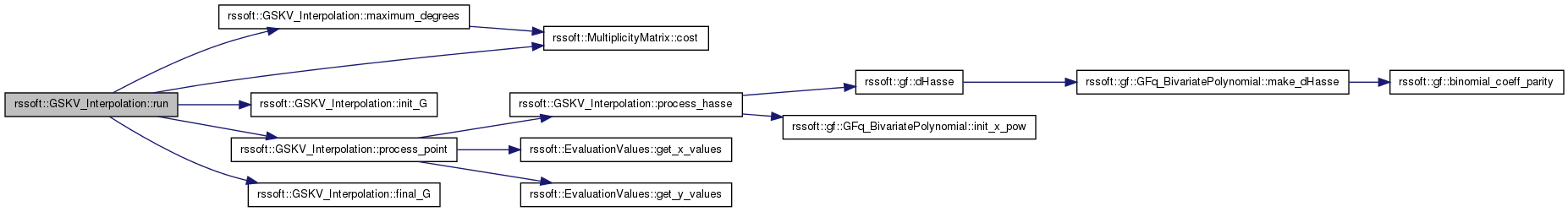
| const gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial & rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::run | ( | const MultiplicityMatrix & | mmat | ) |
Run the interpolation based on given multiplicity matrix
{
std::pair<unsigned int, unsigned int> max_degrees = maximum_degrees(mmat);
dX = max_degrees.first;
dY = max_degrees.second;
mcost = mmat.cost();
//DebugMsg(0,verbose) << "dX = ";
//DebugStream() << "dX = " << "toto" << std::endl;
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 0, "dX = " << dX << ", dY = " << dY << std::endl);
init_G(dY);
it_number = 0;
Cm = mmat.cost();
// outer loop on multiplicity matrix elements
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 0, "Loop on multiplicity matrix elements:" << std::endl);
MultiplicityMatrix::traversing_iterator m_it(mmat.begin());
for (; m_it != mmat.end(); ++m_it)
{
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 0, "*** New point iX = " << m_it.iX() << " iY = " << m_it.iY() << " mult = " << m_it.multiplicity() << std::endl);
process_point(m_it.iX(), m_it.iY(), m_it.multiplicity());
}
const gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial& Q = final_G();
DEBUG_OUT(verbosity > 0, "Q(X,Y) = " << Q << std::endl);
return Q;
}
| void rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::set_verbosity | ( | unsigned int | _verbosity | ) | [inline] |
Set or reset verbose mode.
| _verbose | Verbose level. 0 to shut down any debug message. Active only in debug mode (_DEBUG defined) |
{
verbosity = _verbosity;
}
std::vector<bool> rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::calcG [protected] |
Li Chen's optimization. If true the corresponding polynomial in G is processed.
unsigned int rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::Cm [protected] |
Cost of current multiplicity matrix.
unsigned int rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::dX [protected] |
unsigned int rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::dY [protected] |
const EvaluationValues& rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::evaluation_values [protected] |
Interpolation X,Y values.
unsigned int rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::final_ig [protected] |
Index of the result polynomial in G list.
std::vector<gf::GFq_BivariatePolynomial> rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::G [protected] |
The G list of polynomials.
const gf::GFq& rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::gf [protected] |
Reference to the Galois Field being used.
unsigned int rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::it_number [protected] |
Hasse derivative iteration number (inner loop)
unsigned int rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::k [protected] |
k factor as in RS(n,k)
std::vector<unsigned int> rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::lodG [protected] |
Leading orders of polynomials in G.
unsigned int rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::mcost [protected] |
Multiplicity matrix cost.
unsigned int rssoft::GSKV_Interpolation::verbosity [protected] |
Verbose level, 0 to shut down any debug message.